Languages / Idiomas / Idiomes

Home > AN-VR-ABMT: Attentional bias modification, using virtual reality, to improve the treatment of anorexia nervosa
AN-VR-ABMT: Attentional bias modification, using virtual reality, to improve the treatment of anorexia nervosa
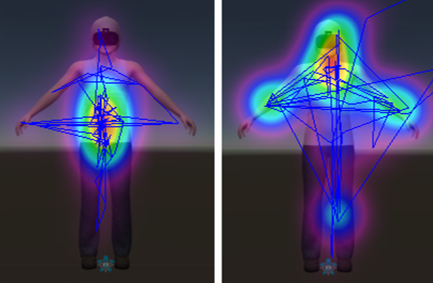
AN-VR-ABMT: Attentional bias modification, using virtual reality, to improve the treatment of anorexia nervosa.
Author: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger Annweiler
Director: José Gutiérrez Maldonado
Institution: Universitat de Barcelona
Year: 2024
Collaborating entities: This study was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (Agencia Estatal de Investigación, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain). Grant PID2019-108657RB-I00 funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033. This study also has the support of “Fundació La Marató de TV3”, Grant 202217-10.
Project
Publications
Abstract: Mirror exposure therapies (METs) have been shown to be effective in reducing body image
disturbances through the habituation process. Virtual reality (VR) combined with eye-tracking
techniques can provide innovative solutions to some of METs’ limitations reported with patients
with anorexia nervosa (AN), especially the negative influence of body-related attentional bias (AB).
This pilot study aimed to assess the preliminary efficacy of a new VR-based AB modification task
(ABMT) among healthy women and the procedure’s user experience. AB levels towards weight- and
non-weight-related body parts, using complete fixation time (CFT) and number of fixations (NF),
were assessed throughout the ABMT procedure (300 trials). The user experience was evaluated at
the end of the procedure. The results showed that VR-based ABMT was effective in reducing AB
significantly after 150 trials for both CFT- and NF-based measures, although 225 trials were necessary
to get the same result for women with an NF initially more oriented towards weight-related body
parts. Overall, the software received a “C-rating” on a scale from “A” (most usable) to “F” (least
usable). These results provide evidence of the opportunity to use a VR-based ABMT procedure to
reduce AB and improve existing treatments for AN.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Marta Ferrer-Garcia,
Manuel Moreno-Sanchez, Helena Miquel-Nabau, Eduardo Serrano-Troncoso, Marta Carulla-Roig and José Gutiérrez-Maldonado
Journal: Journal of Clinical Medicine
Year: 2023
Abstract: Body dissatisfaction, fear of gaining weight (FGW) and body anxiety have been extensively studied as some of the strongest risk and maintenance factors of anorexia nervosa (AN) symptomatology. Recently, a new theoretical model introduced self-disgust as a factor that can lead to avoidance behaviors when patients with AN face their body. This can make them vulnerable to relapse. In addition, body-related attentional bias (AB) (e.g., selective attention to weight-related body areas) can limit the efficacy of body exposure therapies. This study aims to investigate the possible predictors of AB, to better understand the underlying mechanisms that contribute to the maintenance of AN symptomatology. A total of 116 college students from the University of Barcelona participated in the study, using a combination of virtual reality and eye-tracking techniques to provide an objective and reliable assessment of AB in a highly realistic environment. Stepwise multiple linear regression analyses were performed to identify possible predictors of AB among body mass index, FGW, body anxiety, body dissatisfaction and self-disgust. The results shows that both body dissatisfaction and self-disgust are significant predictors of AB. While an increase in body dissatisfaction predicted a greater AB towards weight-related body areas (positive regression coefficients: BBody_dissatisfaction→AB > 0, p < .001), the opposite occurred with self-disgust (negative regression coefficients: BSelf_disgust→AB < 0, p < .02). Such results provide initial evidence that self-disgust, which is a more intense negative feeling than body dissatisfaction, leads to gaze avoidance towards weight-related body areas, which are considered disgust elicitors.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Julia Prieto-Perpiña, Chiara Verdasco, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and José Gutiérrez-Maldonado
Journal: Annual Review of Cyberherapy and Telemedicine 2023 (pp. 76-82)
Year: 2023
Abstract: Background: Body dissatisfaction (BD) has been consistently linked to adverse consequences
on mental health and overall well-being, and is recognized as a significant contributing factor
in the initiation and persistence of eating disorders (EDs). Empirical evidence has demonstrated that
an elevated body mass index (BMI) and media influence and pressure about a thin ideal heighten
the risk of subsequent BD. Moreover, suggestibility, a propensity to accept and act upon messages
without critical evaluation, has been shown to be positively associated with greater susceptibility
to the influence of sociocultural messages that endorse the thin ideal. This study aimed to assess
whether suggestibility moderates the association between BMI and BD in women. Methods: A total
of 117 women completed assessments using the Eating Disorder Inventory-3 (EDI-3) BD subscale and
the Suggestibility Inventory, which encompasses a general suggestibility index and a subscale that
evaluates susceptibility to influence by others. We conducted moderation analyses employing the
PROCESS macro, with BMI as the central predictor, BD as the outcome variable, and suggestibility
and its subscale as moderators. Results: The findings revealed statistically significant positive moderating
interactions for both the general suggestibility index and susceptibility to influence by others.
Specifically, women who exhibited high levels of suggestibility and susceptibility to influence by
others demonstrated a more pronounced increase in BD as their BMI increased. Conclusions: These
outcomes are in line with the sociocultural model of EDs, suggesting that greater susceptibility to
external influences amplifies the impact of societal pressures to conform to thin ideals.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Maria-Teresa Mendoza-Medialdea, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Journal: Journal of Clinical Medicine
Year: 2024
Abstract: The application of advanced embodied technologies, particularly virtual reality (VR), has been suggested as a means to
induce the full-body illusion (FBI). This technology is employed to modify different facets of bodily self-consciousness,
which involves the sense of inhabiting a physical form, and is influenced by cognitive inputs, affective factors like body dissatisfaction,
individual personality traits and suggestibility. Specifically, VR-based Mirror Exposure Therapies are used for
the treatment of anorexia nervosa (AN). This study aims to investigate whether the “Big Five” personality dimensions, suggestibility,
body dissatisfaction and/or body mass index can act as predictors for FBI, either directly or acting as a mediator,
in young women of similar gender and age as most patients with AN. The FBI of 156 healthy young women immersed in VR
environment was induced through visuomotor and visuo-tactile stimulations, and then assessed using the Avatar Embodiment
Questionnaire, comprising four dimensions: Appearance, Ownership, Response, and Multi-Sensory. Data analysis encompassed
multiple linear regressions and SPSS PROCESS macro’s mediation model. The findings revealed that the “Big Five”
personality dimensions did not directly predict FBI in healthy young women, but Openness to experience, Agreeableness,
and Neuroticism exerted an indirect influence on some FBI components through the mediation of suggestibility.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Maria-Teresa Mendoza-Medialdea, Julia Prieto- Perpiña, Adela Fuste-Escolano, Jose Ruiz-Rodriguez, Marta Ferrer-Garcia, and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Journal: Virtual Reality (Springer)
Year: 2024
Abstract: pending publication, coming soon.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Maria-Teresa Mendoza-Medialdea, Eduardo Serrano- Troncoso, Marta Carulla-Roig, Marta Ferrer-Garcia, and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Abstract: pending publication, coming soon.
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Marta Carulla-Roig, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Eduardo Serrano-Troncoso, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and José Gutierrez-Maldonado
Oral communications on conferences
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Marta Carulla-Roig, Helena Miquel-Nabau, Eduardo Serrano-Troncoso, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Conference: VR Mental Health Conference 2023
City and dates: Groningen, November, 9-10, 2023
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Maria-Teresa Mendoza-Medialdea, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Conference: VR Mental Health Conference 2023
City and dates: Groningen, November 9-10, 2023
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Julia Prieto-Perpiña, Chiara Verdesca, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and José Gutierrez-Maldonado
Conference: 26th Annual Cyberpsychology, Cybertherapy and Social Networking Conference (cypsy26)
City and dates: Paris, July, 11-13, 2023
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Mariarca Ascione, Bruno Porras-Garcial, Helena Miquel, Erik Exposito, Eduardo Serrano-Troncoso, Marta Carulla-Roig, Marta Ferrer-Garcia, Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Conference: European Congress of Psychiatry - EPA 2023
City and dates: Paris, March, 25-28, 2023
Authors: Meschberger-Annweiler, Franck-Alexandre; Ascione, Mariarca; Miquel, Helena; Porras-Garcia, Bruno;
Exposito, Erik; Serrano-Troncosa, Eduardo; Carulla-Roig, Marta; Ferrer-Garcia, Marta; Gutierrez-Maldonado, Jose
Conference: International Multi-Brain Congress
City and dates: Barcelona, November, 9-10, 2022
Authors: Franck-Alexandre Meschberger-Annweiler, Bruno Porras-Garcia, Mariarca Ascione, Helena Miquel, Eduardo Serrano-Troncoso, Marta Carulla-Roig, Marta Ferrer-Garcia and Jose Gutierrez-Maldonado
Conference: International Congress of Eating Disorders (ICED) 2022
City and dates: Virtual event, June, 9-10, 2022