Power Spectrum and Bispectrum BOSS DR12
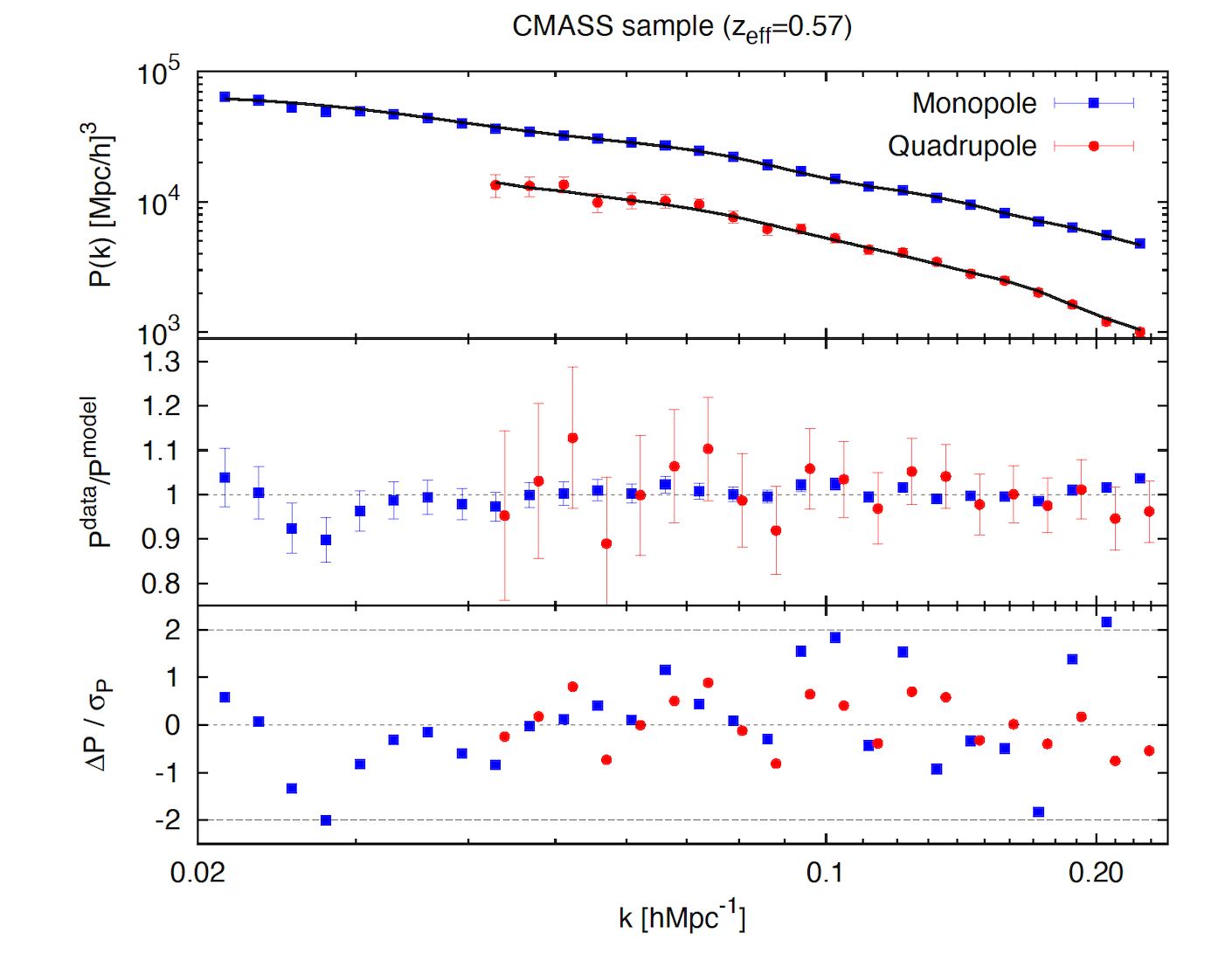
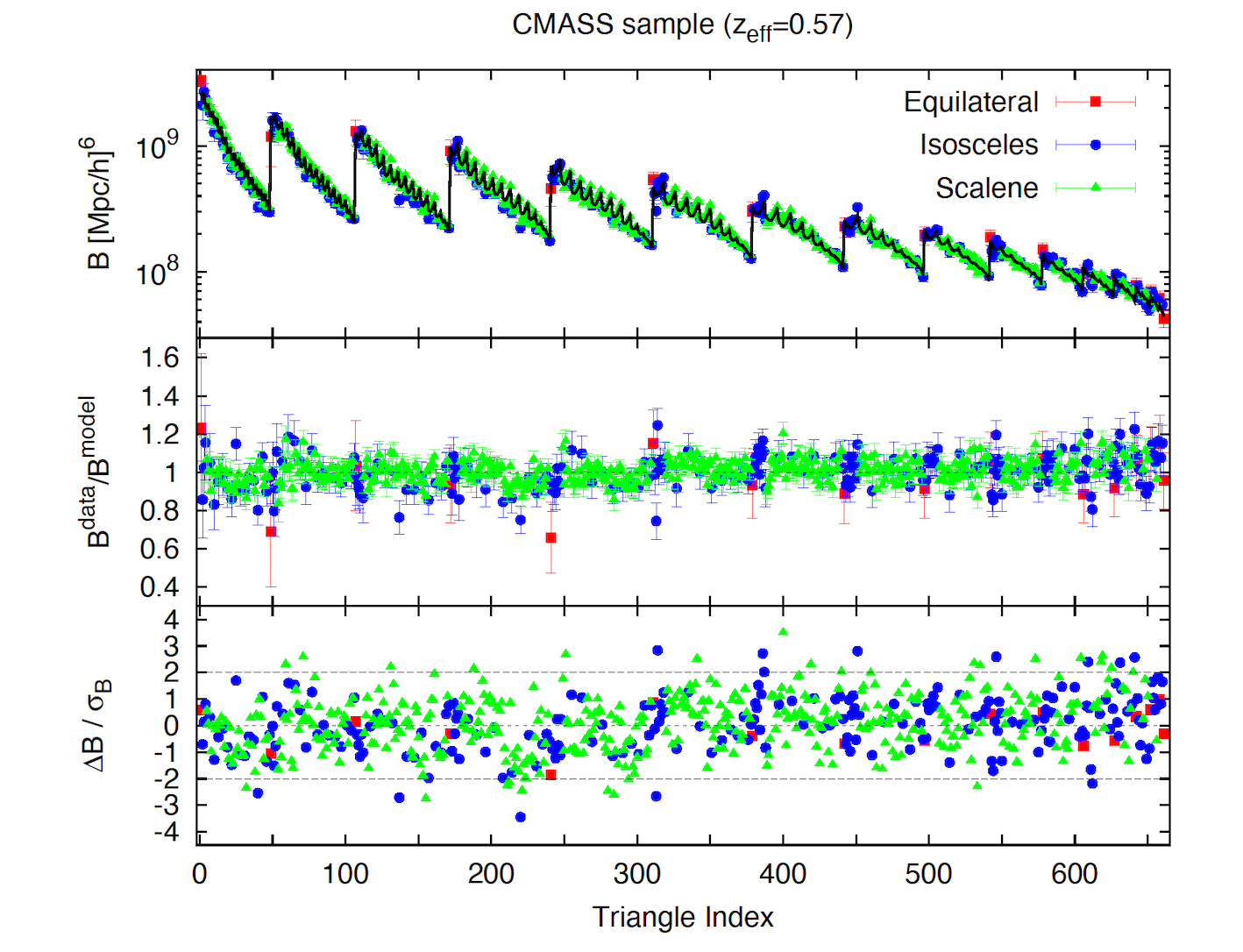
The power spectrum and bispectrum (the two- and three-point correlation function in Fourier space) are the statistics used to extract cosmological information from galaxy surveys. Traditionally only the power spectrum has been used as it is simpler to measure and model than higher order statistics.
However the bispectrum encloses key information highly complementary to that enclosed in the power spectrum, so there has recently been a significant effort to consider also bispectrum data in cosmological analyses.
We provide the power spectrum and bispectrum measurements of the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) Data Release 12, galaxy sample, split by selection algorithm into LOWZ (0.15 <z<0.43) and CMASS (0.43<z<0.70) galaxies. The LOWZ sample contains 361,762 galaxies with an effective redshift of 0.32, and the CMASS sample 777,202 galaxies with an effective redshift of 0.57. Combining the power spectrum, measured relative to the line-of-sight, with the spherically averaged bispectrum, one can put constrains on the product of the growth of structure parameter f, and the amplitude of dark matter density fluctuations, sigma8, along with the geometric Alcock-Paczynski parameters, the product of the Hubble constant and the comoving sound horizon at the baryon drag epoch, and the angular distance parameter divided by the sound horizon.
The readme file documentation explains what is in each of the associated files: Public Files.
The power spectrum pre-, post-reconstruction power spectrum and pre-reconstruction bispectrum data provided correspond to those used in Gil-Marin et al. 2016a, Gil-Marin et al. 2016b and Gil-Marin et al. 2017, respectively. Please cite these papers if you are using this data.
We also make publicly available the best-fitting values of α parallel and perpendicular, along with fσ8 using the modeling desribed in the above papers, for both data and the 2048 MD-Patchy catalogues, LOWZ and CMASS, pre- and post-recontruction. The pre-reconstructed catalogues correspond to a Full Shape or RSD analysis including the power spectrum monopole and quadrupole (Best-fitting values, described in Gil-Marin et al. 2016a); and also adding the bispectrum monopole (Best-fitting values, described in Gil-Marin et al. 2017). The post-reconstructed catalogues correspond to a BAO analysis (Best-fitting values, described in Gil-Marin et al. 2016b).
For the RSD analyses the fiducial cosmology is the one described in sec 2.3 of any of the above RSD-papers, and correspond to the following CAMB file: RSD params file, RSD Plin file.
For the BAO analysis the fiducial cosmology is the one quoted in table 1 of the BAO-paper and correspond to the following CAMB file: BAO params file, BAO Plin file.
Note that in case you want to use simultaneously the α-products of both RSD and BAO analyses you need to re-scale the α values of one of the analysis into the other's fiducial cosmology. Since these two cosmologies have the same Om^fid the scaling factor (for all α) is just (H0*rs)^rsd/(H0*rs)^bao=0.988136. In particular we have done so for the BAO best-fitting αs, which has been re-scaled to the RSD fiducial template: Best-fitting BAO-α values re-scaled to RSD-fiducial.
More public BOSS products (including partially the products available also on this site) can be found in the official BOSS public pages. For citing policies please check How to cite SDSS, and in particular please add in your paper the Official SDSS-III Acknowledgment.

Hector Gil-Marin, 17 Feb. 2020.




